Atmospherics
From Unofficial Stationeers Wiki
This page contains outdated information on the Atmospherics Kit, and should not be used as is. The entire page needs to be rewritten to be valid again!
 | |
| Properties | |
|---|---|
| Stacks | False |
| Recipe | |
| Created With | Hydraulic Pipe Bender, Fabricator |
| Cost | 10g Iron, 5g Gold, 20g Copper |
Air Conditioner Unit
 | |
| Operation | |
|---|---|
| Power Usage | Up to 7000W based on temperature difference |
| Construction | |
| Placed with | Kit (Atmospherics) |
| Placed on | Small Grid |
| Stage 1 | |
| Deconstruction | |
| Deconstructed with | Hand Drill |
| Item received | Kit (Atmospherics) |
Description
Used to lower or raise the temperature of Gas in a pipe network. It has a range of -200 through 200 Celsius for the temperature output.
Usage
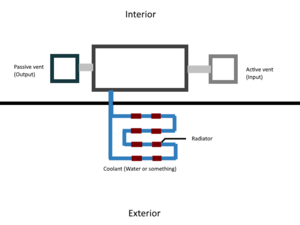
Once you have placed the Air Conditioner Unit in your desired location, there are 3 separate connections that will need to be made:
- Input - The starting gas that is desired to be cooled or heated
- Output - The exhausted gas after energy has been transferred to or from the Coolant in the waste pipe network
- Waste - Connection where energy is transferred to the Coolant in the pipe network
Waste Pipe Network
A connected gas pipe network containing any desired Coolant. The Air Conditioner Unit will draw or expel heat from/to the coolant to adjust the input gas temperature to match the selected output temperature.
If the waste pipe network is below 100kPa pressure upon starting the Air Conditioning Unit, it will divert inputted gas from the output port to the waste port until the minimum 100kPa pressure threshold is met within the waste pipe network.
Cooling
Attached to the waste pipe network should be either Pipe Radiators or Medium Radiators to convect heat in a pressurized environment or radiate heat in a vacuum environment. Make the pipe network loop on back to the waste port after the radiators for slightly better efficiency.
Heating
Attaching a Pipe Heater is a quick method of raising the temperature of the Coolant in the waste pipe network. Ensuring the temperature of the coolant is higher than the temperature of the gas you want attempting to heat will allow the Air Conditioner Unit to heat the gas being run through the input port.
Data Network Properties
These are all Data Network properties of this device.
Data Parameters
These are all parameters that can be written with a Logic Writer, Batch Writer, or Integrated Circuit (IC10).
| Parameter Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Open | Boolean | Starts the Air Conditioner Unit, when set to 1. Stops it, when set to 0. (This seems to work only with Batch Writer and not with Logic Writer - tested on game ver: v0.1.1362.6552). |
| Mode | Integer | (Unknown) (Judging by the "Mode" output, it accepts values in the range 0-2.) |
| Lock | Boolean | Locks the Air Conditioner Unit, when set to 1. Unlocks it, when set to 0. |
| On | Boolean | Turns the Air Conditioner Unit on, when set to 1. Turns it off, when set to 0. |
Data Outputs
These are all parameters, that can be read with a Logic Reader or a Slot Reader. The outputs are listed in the order a Logic Reader's "VAR" setting cycles through them.
| Output Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Power | Boolean | Returns whether the Air Conditioner Unit is turned on and receives power. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| Open | Boolean | Returns whether the Air Conditioner Unit is running. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| Mode | Integer | (Unknown) (Returns output in the range 0-2, equivalent to the input of the "Mode" parameter.) |
| Error | Boolean | Returns whether the Air Conditioner Unit is flashing an error. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| Lock | Boolean | Returns whether the Air Conditioner Unit is locked. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| On | Boolean | Returns whether the Air Conditioner Unit is turned on. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| RequiredPower | Integer | Returns the current amount of power, required by the Air Conditioner, in Watts. |
Filtration
 | |
| Operation | |
|---|---|
| Power Usage | 10W |
| Construction | |
| Placed with | Kit (Atmospherics) |
| Placed on | Small Grid |
| Stage 1 | |
| Deconstruction | |
| Deconstructed with | Hand Drill |
| Item received | Kit (Atmospherics) |
Description
Used to separate gasses from one pipe network into another using filters. Can filter up to two (2) gases at once.
Usage
Place the Kit (Atmospherics) and change the variant to Filtration.
Place filters in the machine for what you want to filter out.
There are three filtration pipe connections.
Filtration Input is where you connect the incoming atmosphere to be passed through the Filtration Atmospherics.
Filtration Unfiltered is the remaining mix after extracting whatever the filters did.
Filtration Filtered is the filtered material for which you placed filters in the machine for.
Be aware that the filtration unit unrealistically has an infinitely powerful pump integrated into its output port. That means as long as it is turned on and there is gas to filter out from the input it will pump that filtered out gas into the output pipe network (no matter how high the pressure in that output pipe network already is!). So eventually that pipe network will burst (around 60 MPa) unless you provide some sort of pop-off valve (e.g. a combination of a back-pressure regulator and a passive vent) or use a pipe analyzer and some logic to turn the filtration unit off when a certain amount of pressure is exceeded in the output pipe network. The filtration system can handle an input gas flow of just over 2.3L from a volume pump.
Data Network Properties
These are all Data Network properties of this device.
Data Parameters
These are all parameters that can be written with a Logic Writer, Batch Writer, or Integrated Circuit (IC10).
| Parameter Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| On | Boolean | Turns the Filtration Unit on, when set to 1. Turns it off, when set to 0. |
Data Outputs
These are all parameters, that can be read with a Logic Reader or a Slot Reader. The outputs are listed in the order a Logic Reader's "VAR" setting cycles through them.
Logic
| Output Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Power | Boolean | Returns whether the Filtration Unit is turned on and receives power. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| Error | Boolean | Returns whether the Filtration Unit is flashing an error. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| Lock | Boolean | Returns whether the Filtration Unit is locked. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| Maximum | ||
| Mode | Integer | 0=Idle, 1=Active |
| On | Boolean | Returns whether the Filtration Unit is turned on. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| Open | Boolean | Returns whether the Filtration Unit is flashing an error. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| OperationalTemperatureEfficiency | ||
| RequiredPower | Integer | Returns the current amount of power, required by the Filtration Unit, in Watts. |
| PrefabHash | Integer | The Hash of the structure. |
| PressureEfficiency | Float | |
| CombustionInput | ||
| CombustionOutput | ||
| CombustionOutput2 | ||
| PressureInput | Float | the pressure on the input pipe |
| PressureOutput | Float | the pressure on the filtered output pipe |
| PressureOutput2 | Float | the pressure on the waste output pipe |
| Ratio | Float | |
| RatioCarbonDioxideInput | ||
| RatioCarbonDioxideOutput | ||
| RatioCarbonDioxideOutput2 | ||
| RatioNitrogenInput | ||
| RatioNitrogenOutput | ||
| RatioNitrogenOutput2 | ||
| RatioNitrousOxideInput | ||
| RatioNitrousOxideOutput | ||
| RatioNitrousOxideOutput2 | ||
| RatioOxygenInput | ||
| RatioOxygenOutput | ||
| RatioOxygenOutput2 | ||
| RatioPollutantInput | ||
| RatioPollutantOutput | ||
| RatioPollutantOutput2 | ||
| RatioVolatilesInput | ||
| RatioVolatilesOuput | ||
| RatioVolatilesOuput2 | ||
| RatioWaterInput | ||
| RatioWaterOutput | ||
| RatioWaterOutput2 | ||
| Setting | ||
| TemperatureDifferencialEfficiency | Float | a value from 0..1.0 indicating the efficiency based on the temperature differential between the "waste" output and the conditioned air stream. This is not updated while the unit is Idle. |
| TemperatureInput | ||
| TemeratureOutput | ||
| TemeratureOutput2 | ||
| TotalMolesInput | ||
| TotalMolesOutput | ||
| TotalMolesOutput2 |
Logic Slots
Slot 0 and 1 are the two gas filters. Slot 2 is the programmable chip
| Output Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Occupied | Boolean | Returns whether the slot is occupied. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| OccupantHash | Integer | Returns the hash of the object in the slot. |
| Quantity | Integer | Returns the current quantity, such as stack size, of the item in the slot. |
| Damage | Integer | Returns the damage state of the item in the slot. |
| Class | Integer | Returns an integer representing the class of object. |
| MaxQuanity | Integer | Returns max stack size of the item in the slot. |
| PrefabHash | Integer | Returns the hash of the structure in the slot. |
Electrolyzer
 | |
| Operation | |
|---|---|
| Power Usage | 1200W |
| Construction | |
| Placed with | Kit (Atmospherics) |
| Placed on | Small Grid |
| Stage 1 | |
| Deconstruction | |
| Deconstructed with | Hand Drill |
| Item received | Kit (Atmospherics) |
Description
Used to separate water (H2O) into H2 and O2 in a 2 to 1 ratio (perfect fuel).
Usage
Place the Kit (Atmospherics) and change the variant to Electrolyzer.
There are two pipe connections.
Electrolyzer Input is where you connect the incoming water.
Electrolyzer Output is where the H2 and O2 comes out mixed together.
Data Network Properties
These are all Data Network properties of this device.
Data Parameters
These are all parameters that can be written with a Logic Writer, Batch Writer, or Integrated Circuit (IC10).
| Parameter Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Lock | Boolean | Locks the Electrolyzer , when set to 1. Unlocks it, when set to 0. |
| On | Boolean | Turns the Electrolyzer on, when set to 1. Turns it off, when set to 0. |
Data Outputs
These are all parameters, that can be read with a Logic Reader or a Slot Reader. The outputs are listed in the order a Logic Reader's "VAR" setting cycles through them.
| Output Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Power | Boolean | Returns whether the Electrolyzer is turned on and receives power. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| Error | Boolean | Returns whether the Electrolyzer is flashing an error. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| Lock | Boolean | Returns whether the Electrolyzer is locked. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| On | Boolean | Returns whether the Electrolyzer is turned on. (0 for no, 1 for yes) |
| RequiredPower | Integer | Returns the current amount of power, required by the Electrolyzer, in Watts. |
Hydrogen Combustor
The hydrogen combustor takes a fuel mix (H2+O2), and generates water, a *lot* of heat, and waste gasses.
Limiting inflow is *highly* recommended, due to the massive amounts of heat generated.