Air Conditioner
From Unofficial Stationeers Wiki
 | |
| Operation | |
|---|---|
| Power Usage | 10W + 340W when active |
| Prefab Hash | -2087593337 |
| Prefab Name | StructureAirConditioner |
| Construction | |
| Placed with | Kit (Atmospherics) |
| Placed on | Small Grid |
| Stage 1 | |
| Next Stage Construction | |
| Constructed with item | 2 x Kit (Pipe) |
| Deconstruction | |
| Deconstructed with | Hand Drill |
| Item received | Kit (Atmospherics) |
| Stage 2 | |
| Next Stage Construction | |
| Constructed with tool | Screwdriver |
| Constructed with item | 2 x Cable Coil |
| Deconstruction | |
| Deconstructed with | Wrench |
| Stage 3 | |
| Deconstruction | |
| Deconstructed with | Hand Drill |
Contents
Description
Used to lower or raise the temperature of Gas in a pipe network. It has a range of -270 through 999 Celsius for the temperature output. Guide (Air Conditioning) provides additional information regarding the function, construction, and operation of an Air Conditioner.
Usage
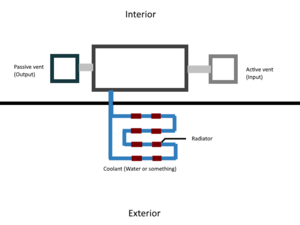
Once you have placed the Air Conditioner Unit in your desired location, there are 3 separate connections that will need to be made:
- Input - The starting gas that is desired to be cooled or heated
- Output - The exhausted gas after energy has been transferred to or from the Coolant in the waste pipe network
- Waste - Connection where energy is transferred to the Coolant in the pipe network
Cooling
The Air Conditioner will take the excess heat from the input gas and transfer it to the Coolant stored in the waste pipe network. Attached to the waste pipe network should be either Pipe Radiators or Medium Radiators to either convect heat in a pressurized environment or radiate heat in a vacuum environment. Make the pipe network loop on back to the waste port after the radiators for slightly better efficiency.
Cooling on Hot Planets
Cooling down to room temperatures (<30°C) on hot planets can be challenging due to the significant temperature difference, which can lead to a decrease in efficiency.
For better cooling results, set up multiple air conditioners in a series. Each air conditioner cools the waste of the previous one, until the last unit expels heat into the environment. This prevents efficiency drops due to high temperature differences.
Use insulated pipes for the of the middle air conditioners for higher efficiency. As a rule, aim for one air conditioner per every 50°C difference in temperature. This keeps cooling effective on hot planets.
On planet Vulcan, consider using high pressure and/or volume for the last pipe network to store cold from the night for the day. An extra room that you can open at night will also help improve efficiency.
Heating
Ensuring the temperature of the coolant is higher than the temperature of the gas you are attempting to heat will allow the Air Conditioner Unit to heat the gas being run through the input port. Attaching a Pipe Heater is a quick method of raising the temperature of the coolant in the waste pipe network.
Waste Pipe Network
A connected gas pipe network containing any desired Coolant. The Air Conditioner Unit will draw or expel heat from/to the coolant to adjust the input gas temperature to match the selected output temperature.
NOTE1: You must pressurize the waste pipe with a coolant gas before the unit will operate.
NOTE2: This image is also out of date. An active vent is no longer required. Two passive vents or two pipe cowls will work just fine for example, saving the 100 W of power an active vent uses and other strangeness with pressurizing the intake side of the pipe.
Characteristics
- It has a manual power switch.
- It has a door on the face of the unit that hides an IC chip slot and the two pins to connect two devices, via logic on the chip.
- It consumes 10W of Power per Tick when idle.
- It consumes 350W of Power per Tick when active.
- Basically, both speed and true efficiency is best at small temperature differences. For large temperature differences, more aircon units need to be put in series.
- It has a separate Power Port and Data Port.
- It has a touchpad that provides manual temperature control.
- It has a pipe port (labelled "Input") for the gases that will be heated or cooled to the designated temperature.
- It has a pipe port (labelled "Output") for the gases that have been heated or cooled to the designated temperature.
- It has a pipe port (labelled "Waste") for gases to or from which heat will be transferred to raise or lower the input gases' temperature.
- Performance drops significantly if the temperature difference becomes too great. Chaining multiple systems, where each aircon cooling/heating the waste pipe of the previous, seems the best way to reach large temperature differences.
- Efficiency changes the effective cooling or heating speed. If it is due to decreasing the volume per tick or J per tick, I do not know.
Efficiency is lost if:
- you want to cool and the waste temp is higher than the input temp (and vice versa)
- Input temperature is outside optimal working temperature from -50 to 100 C.
- input temperature at 400°C ~ 33% efficency
- input temperature at 600°C ~ 10% efficency
- input temperature at 1000°C ~ 0% efficiency
- Efficiency drop due to temperature difference between input and waste is not linear. From 0 difference, efficiency ramps down, after goes straight, and finally levels around T diff ~= 100 (asymptote?) reaching 0% efficiency beyond. Treating it linear anyway, roughly speaking, the efficiency drops 1% per unit temperature difference.
- Efficiency drop due to temperature difference can be negative (>100%), if heat flow is in the working direction, but is low.
NOTE: The information below was left in, in case its still useful. It may not apply to the AC unit in its current form, due to changes in the AC unit. Will require further testing.
- The formula used appears to be: n x T x R = 10123
- n = the number of moles of gas processed
- T = input pipe temperature
- R = 8.3144
- The formula used appears to be: n x T x R = 10123
- Once the amount of processed gas is known, the output temperature can be calculated
- T2 = T1 - 6000 / (n x H)
- T2 = output processed gas temperature
- T1 = input pipe temperature
- n = number of moles of processed gas, see above
- H = heat capacity of the gas in J/(mol x K), i.e. for CO2 it's 28.2 J/mol*K
- T2 = T1 - 6000 / (n x H)
User Interface
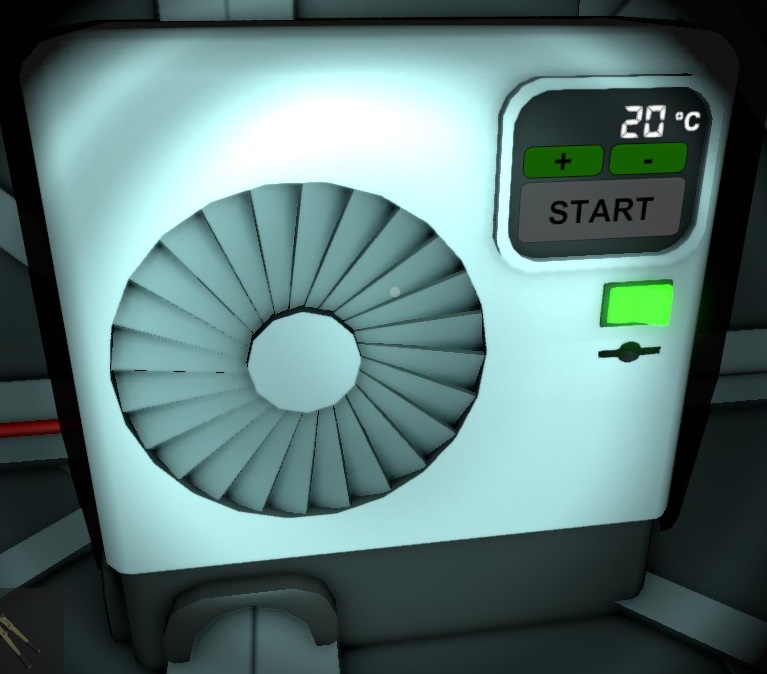
An Air Conditioner provides the following user interface:
| Name | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Display | Displays the current output temperature setting |
| + | Touchkey | Increase the current output temperature setting by 10°C and by 1°C with the Quantity Modifier key pressed. |
| - | Touchkey | Decrease the current output temperature setting by 10°C and by 1°C with the Quantity Modifier key pressed. |
| Start | Touchkey | Switches Air Conditioner between idle and active. |
| On/Off | Switch | Switches Air Conditioner between turned on or turned off. |
Data Network Properties
These are all Data Network properties of this device.
Data Parameters
These are all parameters that can be written with a Logic Writer, Batch Writer, or Integrated Circuit (IC10), and can be read with a Logic Reader, Batch Reader, or Integrated Circuit (IC10).
| Parameter Name | Data Type | Access | Value | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power | Boolean | Read
|
0 | Unpowered | Can be read to return if the Air Conditioner is correctly powered or not, set via the power system, return 1 if powered and 0 if not | |
| 1 | Powered | |||||
| Open | Integer | Read Write
|
0 | Closed | Returns whether the Air Conditioner's IC Slot cover is open or closed. | |
| 1 | Open | |||||
| Mode | Integer | Read Write
|
0 | Idle | The mode of the Air Conditioner. | |
| 1 | Active | |||||
| Error | Boolean | Read
|
0 | 1 if device is in error state, otherwise 0 | ||
| 1 | Error | |||||
| Lock | Boolean | Read Write
|
0 | Unlocked | Disable manual operation of the Air Conditioner. | |
| 1 | Locked | |||||
| Setting | Integer | Read Write
|
||||
| Maximum | Float | Read
|
||||
| Ratio | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| On | Boolean | Read Write
|
0 | Off | The current state of the Air Conditioner. | |
| 1 | On | |||||
| RequiredPower | Integer | Read
|
||||
| PrefabHash | Integer | Read
|
||||
| PressureInput | Float | Read
|
||||
| TemperatureInput | Float | Read
|
||||
| RatioOxygenInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioCarbonDioxideInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioNitrogenInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioPollutantInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioVolatilesInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioWaterInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioNitrousOxideInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| TotalMolesInput | Float | Read
|
||||
| PressureOutput | Float | Read
|
||||
| TemperatureOutput | Float | Read
|
||||
| RatioOxygenOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioCarbonDioxideOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioNitrogenOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioPollutantOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioVolatilesOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioWaterOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioNitrousOxideOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| TotalMolesOutput | Float | Read
|
||||
| PressureOutput2 | Float | Read
|
||||
| TemperatureOutput2 | Float | Read
|
||||
| RatioOxygenOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioCarbonDioxideOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioNitrogenOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioPollutantOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioVolatilesOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioWaterOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioNitrousOxideOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| TotalMolesOutput2 | Integer | Read
|
||||
| CombustionInput | Boolean | Read
|
0 or 1 | |||
| CombustionOutput | Boolean | Read
|
0 or 1 | |||
| CombustionOutput2 | Boolean | Read
|
0 or 1 | |||
| OperationalTemperatureEfficiency | Float | Read
|
||||
| TemperatureDifferentialEfficiency | Float | Read
|
||||
| PressureEfficiency | Float | Read
|
||||
| RatioLiquidNitrogenInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidNitrogenOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidNitrogenOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidOxygenInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidOxygenOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidOxygenOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidVolatilesInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidVolatilesOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidVolatilesOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioSteamInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioSteamOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioSteamOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidCarbonDioxideInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidCarbonDioxideOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidCarbonDioxideOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidPollutantInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidPollutantOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidPollutantOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidNitrousOxideInput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidNitrousOxideOutput | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| RatioLiquidNitrousOxideOutput2 | Float | Read
|
0.0 to 1.0 | |||
| ReferenceId | Integer | Read
|
||||
| NameHash | Integer | Read
|
||||